Summary
LlamaRisk supports onboarding tBTC to Aave V3 on Arbitrum. Since our last analysis, the tBTC supply and liquidity on Arbitrum have improved significantly—a welcome change. However, the tBTC exchange rate on secondary markets (Uniswap pools) has occasionally deviated from the BTC price by a few percent, emphasizing the importance of using the BTC/USD Chainlink feed, as is done on mainnet. Although tBTC-V2 contracts have undergone multiple audits, the Arbitrum cross-chain contracts have not been publicly audited, and reliance on permissioned Beta Stakers, Minters, and Guardians introduces risks of malicious behavior that could disrupt the minting and deposit process and have knock-on effects in lending markets. Furthermore, the Threshold Network’s Bug Bounty program with ImmuneFi offers rewards of up to $500,000 for identifying vulnerabilities, reinforcing the network’s commitment to security.
Collateral Risk Assessment
Collateral Risk Assessment
1. Asset Fundamental Characteristics
1.1 Asset
tBTC (Threshold Bitcoin) is an ERC-20 token backed by Bitcoin 1:1 and pegged to its price. Unlike wBTC, which relies on a centralized custodian, tBTC uses a permissioned signer group that participates in a consensus mechanism to custody the Bitcoin backing it, reducing dependence on centralized third-party custodians.
Contract Address: 0x6c84a8f1c29108F47a79964b5Fe888D4f4D0dE40
As of February 13th, 2025, tBTC has a circulating supply of 94.5 tBTC, with a market capitalization of $9.05 million. The asset does not currently offer a yield. It was launched on March 31st, 2023.
tBTC is an open-source project from Thesis operated by the Threshold Network. It is secured by threshold cryptography and rotates node operators weekly to prevent collusion. tBTC can be minted directly via the Arbitrum Dashboard. Deposits typically take 1-3 hours to be processed and credited. Withdrawals follow a similar process: the tBTC token contract burns the tBTC, and the DepositBridge transfers BTC to the user’s specified Bitcoin address. This process includes a 3-5 hour processing delay.
The platform fees are action-based, with no fee for minting and a 0.2% redemption fee. The accrued tBTC fees are periodically deposited into Threshold-owned Governor Bravo Timelock Controller on the mainnet.
1.2 Architecture
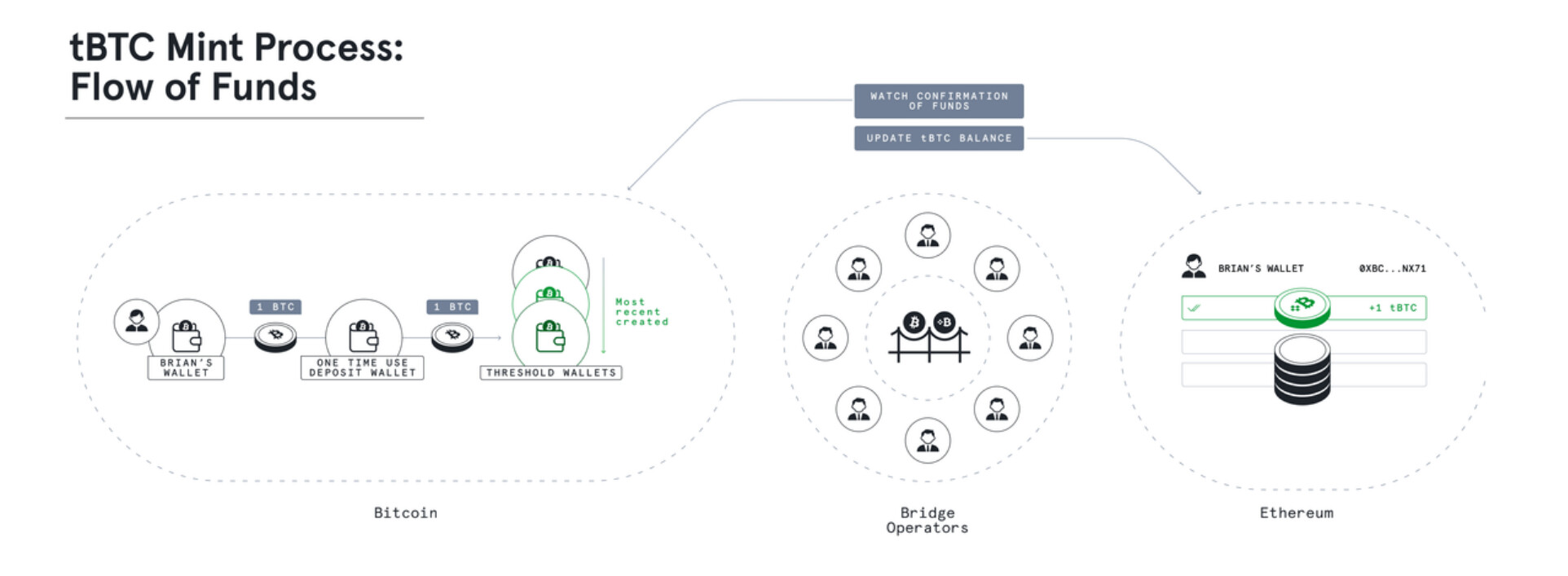
tBTC is a more distributed and decentralized version of existing wrapped Bitcoin tokens as the BTC is not held in custody by private entities but by a decentralized network of node operators. Since the whole process is permissionless, anyone can mint tBTC. The process is as follows: users send their Bitcoin to a one-time-use deposit address → bridge operators move funds to Threshold Wallet and await block confirmation → post confirmation, tBTC is sent to the depositor’s Ethereum address. The list of Threshold operators is publicly available on tBTCscan. Currently, 260 registered node operators are present.
Source: tBTC Flow of Funds, Threshold.
Once the Bitcoin is moved from the deposit address, it goes to a randomly generated wallet by Threshold stakers in Bitcoin wallets controlled by signers participating in the Threshold Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm (ECDSA), which requires 51% of 100 signers to cooperate and sign the transaction. Though the Network operates on Ethereum, signers use an off-chain communication protocol called “libp2p” to coordinate signing events. On each wallet, 100 signers are selected randomly from Keep Network’s Sortition Pool. Random Beacon securely generates random numbers and is used with Threshold Cryptography to impart bias-resistant randomness and thus distribute trust across multiple nodes.
The eligible operators are weighted by their stakes in the Sortition Pool and in the Threshold Network stakers of the “T” token in the Threshold Network are eligible to become signers. The probability of a staker becoming a signer is directly proportional to their share of the total tBTC stake. Each signer is selected independently, meaning the selection of one signer does not influence the chances of another staker being chosen for the same or different wallets. A staker with a higher percentage of the total stake has a correspondingly higher likelihood of being chosen as a signer, and the same staker can be selected multiple times for the same wallet or simultaneously across multiple wallets.
Source: Optimistic Minting Process, Threshold Docs.
The Optimistic minting process is not permissionless, as the 100 signers for each wallet are selected from a restricted list of Beta Stakers rather than the entire pool of Stakers. While this approach was implemented to exclude misbehaving signers and fasten the minting process, Threshold is developing an alternative to allow any staker meeting the required criteria to participate in custodianship.
Source: List of tBTC Guardians and Minters, Threshold.
Guardians and Minters are a permissioned set of high-trust public operators who can be removed through a Threshold DAO vote. Minters approve BTC deposits required for tBTC minting, while Guardians can veto the process, potentially halting growth if a malicious Guardian intervenes. Additionally, a “Sweeping” mechanism (not yet implemented) is designed to allow signers to consolidate unapproved deposits from Guardians every 8 hours, enabling tBTC minting without direct Guardian approval.
Minting on Arbitrum involves depositing BTC into Threshold’s custody on Bitcoin L1, which authorizes tBTC minting on Arbitrum through the tBTC token contract and L2BitcoinDepositor. Redemption requires burning tBTC via the tBTC token contract, after which the BridgeRouter facilitates BTC transfer from a redemption wallet to the user’s provided Bitcoin address. Redemptions have a size limit (based on wallet capacity) and a processing delay of 3-5 hours.
1.3 Tokenomics
Threshold Network’s native token, T, is an ERC-20 token used for staking and governance participation. The total supply is 11.15 billion, with 10.1 billion currently in circulation. Initially, 10 billion tokens were issued, with 4.5 billion allocated to NU and KEEP holders each and 1 billion set aside for the DAO Treasury. The token is inflationary, distributing 15% annual staking rewards to stakers. At network genesis, the minimum stake size was set at 40,000 T. Currently ~3B T tokens ($63M) are staked, representing 27% of the total supply.
1.3.1 Token Holder Concentration
tBTC represents 3.6% of the total BTC on Ethereum. Similarly, tBTC on Arbitrum is an extension of this product, with a total supply of ~95 tBTC, representing 2.17% of tBTC’s total supply (4637 tBTC). Among L2s, Arbitrum has a share of 22.7% tBTC and is second only to Base (262 tBTC) in adoption.
Source: Top 100 tBTC Holders on Arbitrum, Arbiscan, February 13th, 2025.
The top 5 holders of tBTC are:
- Uniswap V3 tBTC/WBTC Pool: 23.27% of the total supply.
- Curve 2BTC-ng tBTC/WBTC Pool: 18.45% of the total supply.
- EOA: 8.62% of the total supply.
- 3/5 Safe Multisig: 7.15% of the total supply.
- Silo Finance tBTC Market: 4.63% of the total supply.
The top 10 holders own 77.54% of the total supply. When considering the top 100 holders, this concentration increases to 99.35%.
2. Market Risk
2.1 Liquidity
Source: tBTC/USDC Swap Slippage, DeFiLlama, February 13th, 2025.
Users can swap up 41 tBTC ($3.95M) for USDC on Arbitrum within a 7.5% price impact.
2.1.1 Liquidity Venue Concentration
Top 5 tBTC DEX liquidity pools by TVL (as of February 13th, 2025):
- Uniswap V3 tBTC/WBTC (0.05% fee): $3.9M
- Curve tBTC/WBTC: $3.16M
- Uniswap V3 tBTC/WETH: $0.54M
- Balancer V2 tBTC/WBTC: $0.33M
- Uniswap V3 tBTC/WBTC (0.01% fee): $0.26M
2.1.2 DEX LP Concentration
LP concentration is moderate; however, Beefy provides significant liquidity. This poses a risk, as liquidity could decline if it’s boosted yields come to an end. Here is the breakdown for the top 5 tBTC pools by TVL (as of February 13th, 2025):
- Uniswap V3 tBTC/WBTC (0.05% fee): The top liquidity provider is an EOA, holding 23% of the pool’s liquidity.
- Curve tBTC/WBTC: 43.3% of the pool’s liquidity is supplied by Beefy.
- Uniswap V3 tBTC/WETH: The top liquidity provider is an EOA, holding 92% of the pool’s liquidity.
- Balancer V2 tBTC/WBTC: 99.3% of the pool’s liquidity is supplied by Beefy.
- Uniswap V3 tBTC/WBTC (0.01% fee): The top liquidity provider is an EOA, holding 40.16% of the pool’s liquidity.
2.2 Volatility
Source: tBTC/BTC Secondary Market Rate, TradingView, February 13th, 2025.
tBTC is trading at a 1.6% discount in secondary markets (Uniswap V3 pools) after trading at a ~2% premium. On multiple occasions, the tBTC/BTC ratio has deviated by over 5%, highlighting volatility driven primarily by low liquidity in secondary markets.
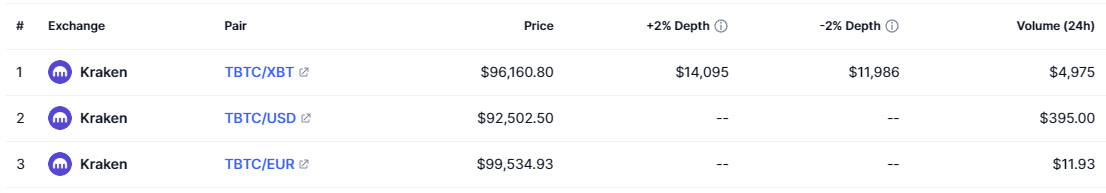
2.3 Exchanges
Source: tBTC CEX Markets, CoinMarketCap, February 13th, 2025.
Kraken is the only centralized exchange listing tBTC, offering three trading pairs. As a result, its trading volume and liquidity remain significantly lower than that of decentralized exchanges, which could pose challenges for large-scale OTC trades or CEX-DEX arbitrage.
2.4 Growth
Source: tBTC Arbitrum Supply, Dune, February 13th, 2025.
Since October 19th, 2024, tBTC supply on Arbitrum (95 tBTC currently) has been in steady decline, with a noticeable liquidity shift away from the network. This coincided with a surge in tBTC growth on Base (262 tBTC), driven by factors like boosted yields from Beefy, a governance proposal to expand tBTC on Base, and SolvBTC minting. These factors, along with the expiration of the 3-month GMX incentives aimed at boosting tBTC DEX liquidity on Arbitrum, further accelerated the decline.
A 30-week loyalty program (September 9th, 2024 - April 7th, 2025) rewarding liquidity providers on Curve and Uniswap pools on Arbitrum is live with a share of 50,000 ARB and a 25% boost in T.
3. Technological Risk
3.1 Smart Contract Risk
The tBTC Bridge V2 contracts have been audited by Least Authority (September 29th, 2022), CertiK (November 19th, 2021) and ChainSecurity (November 9th, 2021).
The audit by Least Authority, dated September 29th, 2022, delved into the security and functionality of the tBTC Bridge v2 with key findings concerned with Bitcoin SPV Merkle Proofs and updates between non-zero allowances. Several suggestions for improvements were also given, most of which were resolved.
Though the smart contracts are verified, the absence of public audits for tBTC contracts on Arbitrum introduces potential security risks.
3.2 Bug bounty program
Threshold Network has a Bug Bounty program with ImmuneFi where anyone can get rewards up to $500,000, depending on the severity of the threat. The contracts in the scope can be found here.
3.3 Price Feed Risk
tBTC on Arbitrum has a TBTC/USD Chainlink price feed with a 24-hour heartbeat and a 0.5% deviation threshold. However, due to limited on-chain liquidity on Arbitrum, as highlighted in the volatility section, the tBTC price feed remains vulnerable to manipulation. The Chainlink’s BTC/USD feed should be used instead to mitigate this risk.
While Threshold Network’s design allows all deposits to be publicly viewable on tBTCscan 24/7, a Chainlink proof-of-reserve (PoR) feed for Bitcoin reserves would enhance reliability and safeguard against potential downtime. As previously discussed for Ethereum markets, we recommend using PoR feeds as a trigger switch for tBTC/USD market pricing on Arbitrum to prevent unnecessary bad debt in the event of insolvency.
3.4 Dependency Risk
Wormhole Dependence
After the recent upgrade launched by Threshold DAO, which launched its first cross-chain native minting experience for tBTC users on Arbitrum, the dependency risk of bridges to transfer tBTC has been eliminated, the native minting on Arbitrum is powered by an off-chain relayer and tBTC SDK extension to Arbitrum. The relayer is powered by Wormhole, a long-standing Threshold DAO member, and it coordinates transactions between chains to allow minting. Threshold DAO members maintain it through governance.
Honest Majority Assumption
The honest majority assumption introduces risks inherent to relying on a randomly selected group of operators to secure deposits. If most of these operators act dishonestly or collude, they could compromise the security of the underlying Bitcoin. While the weekly rotation of operators reduces the risk of sustained collusion, it does not eliminate the possibility of a quorum of dishonest operators being selected in any given round. This makes the system’s security dependent on maintaining a robust and sufficiently decentralized network of trustworthy operators.
Permissioned Stakers
The risk of signers gaining over 51% control of a wallet is limited to the wallets they manage. Measures like permissioned beta stakers help tBTC to mitigate risks, but as the protocol becomes permissionless, a centralized stake could increase the chances of collusion. Decentralized stake distribution remains crucial to minimize the likelihood of majority control by a single party. tBTC operates as a distributed, permissioned protocol, relying on the signer’s reputation to ensure security while avoiding reliance on a single custodian. Transitioning to a permissionless model in the future will add some of these risks that require careful consideration.
4. Counterparty Risk
4.1 Governance and Regulatory Risk
Source: Threshold DAO Governance Proposal Life Cycle, Threshold.
Threshold’s governance includes a Token Holder DAO and an Elected Council, ensuring mutual accountability. All governance votes are publicly viewable on Snapshot. A community member must hold at least 0.25% of the T supply to submit an on-chain proposal, with a quorum set at 1.5% of the total supply. The voting power is evenly distributed, with the combined votes of the top 7 delegates reaching the 50% threshold.
Source: Threshold Governance, Threshold Docs.
Threshold Council Veto Power
The Threshold DAO governs the Threshold Network, encompassing the Token Holder DAO and an Elected Council multi-sig. Though the governance is decentralized, an Elected group of Threshold Council multi-sig holders can veto any proposal. Though the Threshold Council (the multi-sig signature policity threshold is set to 6 of 9) is a trusted constituent of DAO and nine elected individuals are voted once every year, they can censor the network if the threshold is reached on the multi-sig. In terms of software, the Council has control over upgradeable application contracts. Originally, the 9-member Council consisted of 4 elected representatives from the Keep community, 4 from the NuCypher community, and 1 mutually appointed member. In the current third epoch, the elected members are:
| Candidate | Signer Address |
|---|---|
| @Eastban | 0x2844a0d6442034D3027A05635F4224d966C54fD7 |
| @Figue | 0xf35dEE924F483Bc234F09cbfbc8B4488fD06be20 |
| @MrsNuBooty | 0x739730cCb2a34cc83D3e30645002C52bA4B06167 |
| @ZeroInFo56 | 0xe989805835093e37E6b12dCddF718e0481024573 |
| @Vict0r | 0x1Ba899530A89fAb245De9ff6cc23534F4a8A4e58 |
| @JohnPackel | 0x12107242e2FbEd0a503e102751fa6Aa8cB7446eC |
| @nico186 | 0x35B46702C5d1CD36194217Fb92F72B563eFf851A |
| @sap | 0xcE3778528fC73D46685069D455bbCcE16A6e22Af |
| @shoegazer69 | 0xf791EfdF778a3Ca9cc193fFbe57Da33d1596E854 |
4.2 Access Control Risk
4.2.1 Contract Modification Options
Threshold contracts on Arbitrum:
- ArbitrumTBTC: The tBTC ERC-20 contract with role-based minting, burning, token spending, and permissioned recovery functions. The owner can manage addresses authorized to mint tBTC, control Guardian roles, halt the transfers and minting, and withdraw mistakenly sent tokens.
- ArbitrumWormholeGateway:
Regulates minting and burning canonical tBTC via the Wormhole bridge, ensuring only authorized cross-chain transfers modify token supply. Key functions includesendTbtc(burn & transfer),receiveTbtc(mint on verification), and the owner permissions likeupdateGatewayAddressandsetMintingLimit. - L2BitcoinDepositor:
It interacts with ArbitrumWormholeGateway to facilitate the initialization of cross-chain deposits usinginitializeDeposit. The owner has the authority over contract initialization (initialize) and linking the L1BitcoinDepositor (attachL1BitcoinDepositor).
In addition to the listed privileges for each contract, the owner, i.e., Threshold Council’s 6/9 multisig, can transfer or revoke ownership for all the listed contracts using transferOwnership or renounceOwnership.
4.2.2 Timelock Duration and Function
Threshold Network has not configured any timelock on tBTC Arbitrum contract upgrades.
4.2.3 Multisig Threshold / Signer Identity
All tBTC contracts on Ethereum and Arbitrum are owned by Threshold Council’s 6/9 Safe multisig, composed of the elected members we listed above.
Note: This assessment follows the LLR-Aave Framework, a comprehensive methodology for asset onboarding and parameterization in Aave V3. This framework is continuously updated and available here.
5. Aave V3 Specific Parameters
Parameters will be presented jointly with @ChaosLabs
6. Price feed
The BTC/USD Chainlink price feed should be used instead of the tBTC/USD feed to price the asset on Aave V3 Arbitrum market, as low liquidity in secondary markets makes the latter susceptible to manipulation. Additionally, we recommend implementing a trigger switch mechanism, combined with a proof-of-reserve (PoR) feed (currently unavailable), to prevent bad debt, as previously discussed during tBTC’s Ethereum onboarding.
Disclaimer
This review was independently prepared by LlamaRisk, a community-led non-profit decentralized organization funded in part by the Aave DAO. LlamaRisk is not directly affiliated with the protocol(s) reviewed in this assessment and did not receive any compensation from the protocol(s) or their affiliated entities for this work.
The information provided should not be construed as legal, financial, tax, or professional advice.