tBTC (Arbitrum and L2s) technical analysis
Summary
This is a technical analysis of all the smart contracts of the tBTC asset on Arbitrum (and similar L2 architectures) and its main bridge dependencies.
Disclosure: This is not a formal audit, such as those conducted by independent security experts at the request of the Threshold team, but rather an analysis from an Aave technical service provider on various aspects we consider critical to review before introducing a new type of listing. Consequently, like with any security review, this is not an absolute statement that the asset is flawless, only that, in our opinion, we don’t see significant problems with its integration with Aave, apart from different trust points.
Analysis
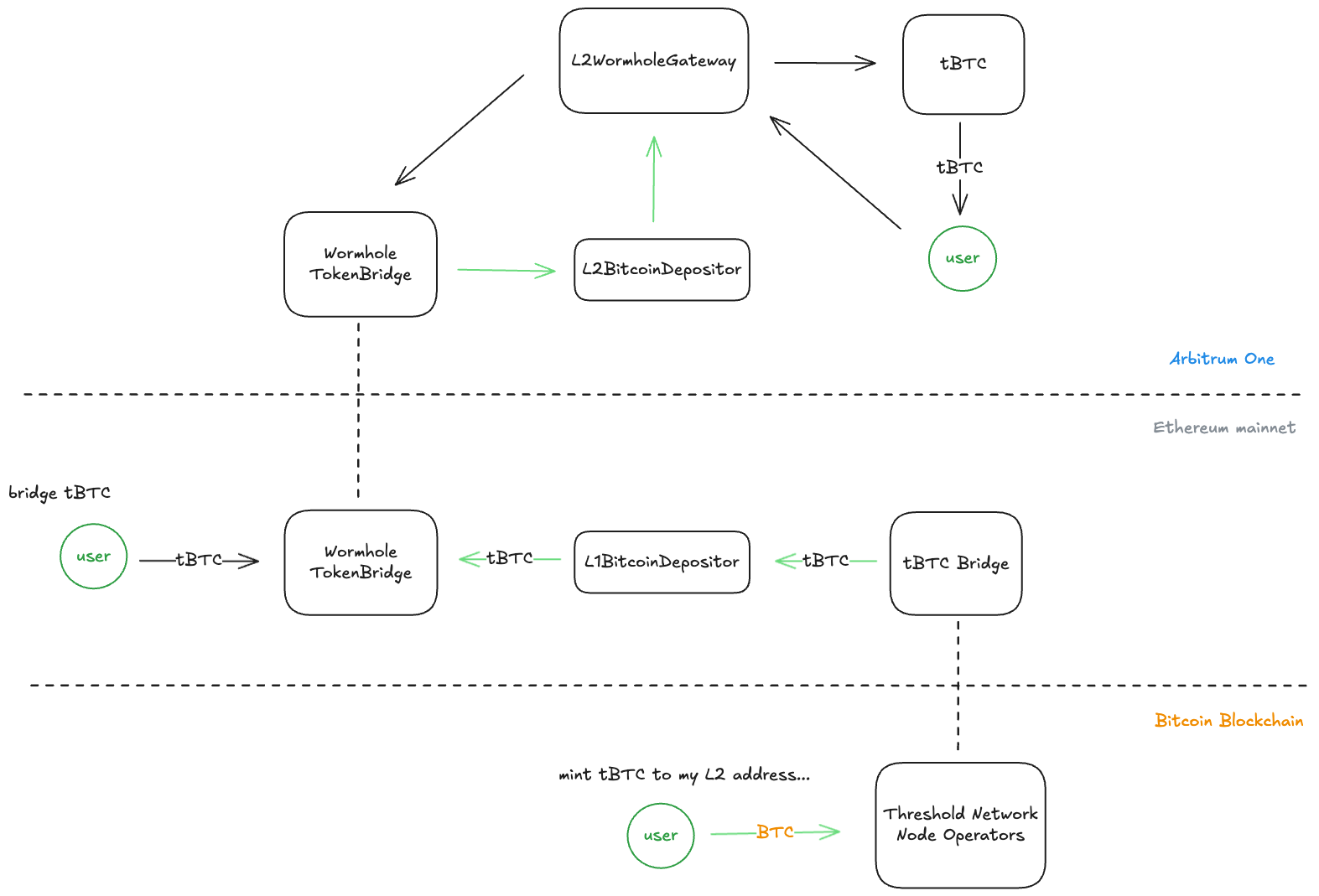
Threshold Team has added support for its cross-chain asset with two different layers:
-
A cross-chain bridge via the Wormhole infrastructure, where tokens are locked in a bridge contract on the mainnet and minted on the respective L2.
-
A “native L2 minting”, where users can follow the same process of issuing a BTC funding transaction to a P2(W)SH deposit address, and instead of giving the user’s L1 address, embeds the L1BitcoinDepositor contract and the user’s L2 address.
Bridge
The main cross-chain tBTC bridge to L2s (Arbitrum in this case) relies on the Wormhole infrastructure. The bridge flow between chains consists of a few steps:
-
L1 → L2s:
-
Users send the tBTC through the Wormhole TokenBridge contract via the
transferTokens()ortransferTokensWithPayload()functions. -
The tBTC is locked in the TokenBridge contract, which sends a cross-chain message.
-
On the L2, the user finalizes the tBTC bridge through the L2WormholeGateway contract by calling the
receiveTbtc()function, which mints a tBTC wormhole representation token to the L2WormholeGateway, and the actual L2 tBTC to the user.
-
-
L2s→ L1
-
Users initiate a cross-chain transfer in the L2WormholeGateway contract via the
sendTbtc()function. -
Internally, the L2 tBTC and the tBTC wormhole representation token amount are burned, and the Wormhole TokenBridge contract is called via the
transferTokens()ortransferTokensWithPayload()functions to send a cross-chain message. -
On the L1, the user finalizes by calling the
completeTransferorcompleteTransferWithPayload()functions in the Wormhole TokenBridge contract, which unlocks the tBTC and sends it to the user.
-
-
L2s → L2:
-
Users initiate a cross-chain transfer in the L2WormholeGateway contract via the
sendTbtc()function. -
Internally, the L2 tBTC and the tBTC wormhole representation token amount are burned, and the Wormhole TokenBridge contract is called via the
transferTokens()ortransferTokensWithPayload()functions to send a cross-chain message. -
On the L2, the user finalizes the tBTC bridge through the L2WormholeGateway contract by calling the
receiveTbtc()function, which mints a tBTC wormhole representation token to the L2WormholeGateway, and the actual L2 tBTC to the user.
-
L2 Minting
The bridge system through the L1BitcoinDepositor and L2BitcoinDepositor contracts allows users to receive tBTC on Arbitrum without needing to interact with the tBTC system in the L1, where the minting occurs.
To achieve the L2 minting, users first need to initiate the same process of depositing BTC into off-chain ECDSA wallets associated with the Bridge, but this time, containing the L1BitcoinDepositor as the actual depositor on the L1 and the L2 user address set as the deposit owner who will receive the tBTC on the L2.
The BTC depositing transaction data and the L2 user’s address are sent via the L2BitcoinDepositor.initializeDeposit(fundingTx, reveal, l2DepositAddr) function in the L2 chain. This function emits a DepositInitialized, which is caught by the relayer to initialize the deposit in the L1 via the L1BitcoinDepositor.initializeDeposit(fundingTx, reveal, l2DepositAddr) function. The L1BitcoinDepositor will reveal the deposit by calling bridge.revealDepositWithExtraData(fundingTx, reveal, extraData) minting the tBTC to the L1BitcoinDepositor contract.
It finishes with the relayer calling the L1BitcoinDepositor.finalizeDeposit(depositKey) function, with the depositKey emitted in the previous step, which will start the cross-chain transfer via the Wormhole TokenBridge contract, following the same steps explained in the L1 → L2 section.
Contracts
Access Control:
The system has ownable access control, which we described below.
-
L1BitcoinDepositor
- Owner can configure gas limit and gas offset parameters, as well as reimbursements, for the cross-chain transaction.
-
L2BitcoinDepositor
- Owner: only initialize the L1BitcoinDepositor contract.
-
L2WormholeGateway
- Owner: can add new gateway contracts for other chains and set minting limits for its own contract (currently, unlimited amount).
-
tBTC
-
Owner: can add/remove minters and guardians, rescue ERC20/ERC721 tokens, and unpause mints and burns.
-
Minters: can mint tBTC
-
Guardians: can pause mints and burns.
-
Ethereum Mainnet
| Contract | Role | Admin | Upgradable |
|---|---|---|---|
| L1BitcoinDepositor | An intermediary contract that receives L1 tBTC to be bridged to an L2 chain | Council Multisig 6-of-9 | ProxyAdmin → 1-day Timelock |
Arbitrum
| Contract | Role | Admin | Upgradable |
|---|---|---|---|
| L2BitcoinDepositor | An intermediary contract that manages the tBTC L2 minting | Council Multisig 6-of-9 | ProxyAdmin → 1-day Timelock |
| L2WormholeGateway | The tBTC minter who interacts with the Wormhole TokenBridge contract | Council Multisig 6-of-9 | ProxyAdmin → 1-day Timelock |
| tBTC | ERC20 token implementation of tBTC | Council Multisig 6-of-9 | ProxyAdmin → 1-day Timelock |
Price strategy
To strictly synchronize the L2 pricing strategy with its price on the L1, we suggest using a BTC/USD Chainlink feed.
Miscellaneous aspects
-
The system has a security review by LeastAuthority and can be found here.
-
As the asset is intended to be listed as collateral, we identified a technical blocker related to the lack of timelocks on certain components (WormholeGateway, L2TBTC, L1BitcoinDepositor and L2BitcoinDepositor). To address this, we requested the Threshold Team to timelock these parts of the system. The team agreed to the request and has implemented the necessary changes.
Conclusion
We believe that tBTC can be integrated with Aave on Arbitrum and future L2 networks without issues, should the DAO choose to proceed, and that there are no technical blockers to listing.